写在前面
本文是afl-fuzz的源码解读部分,这部分内容是整个 AFL 的核心部分,其中涵盖了 AFL 进行 fuzz 的全过程,涉及到了诸多设计思路,因此代码量比较大(8k行左右)。我们会将这些函数进行拆分分析,争取梳理清楚关键函数所处的阶段以及作用。
afl-fuzz
1. 文件描述
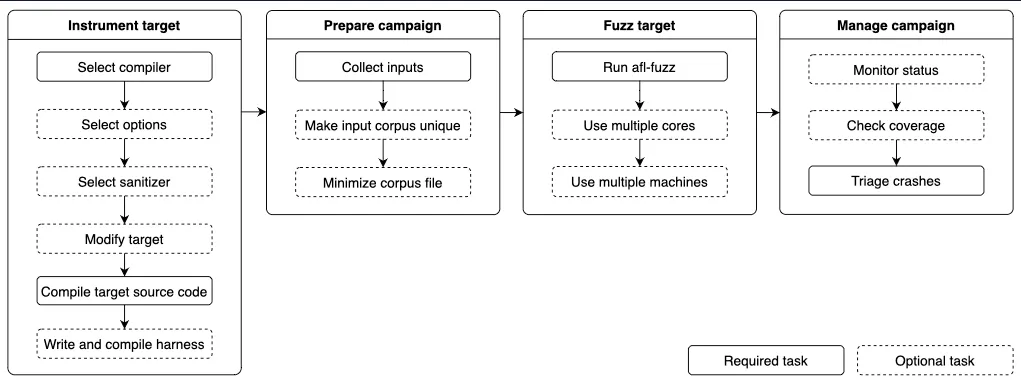
上图是一个基于 AFL 的 fuzz 流程,afl-fuzz.c 文件负责的是 Fuzz target 阶段,主要作用是通过不断变异测试用例来影响程序的执行路径,期间涉及到输入处理 、覆盖率记录、输出记录等等,这些功能是该文件的主要内容。这些功能会涵盖诸多函数,我们不会对每一个函数都进行源码分析,而是按照功能介绍关键函数。
在功能上,可以总体分为3部分:
- 初始设置:进行 fuzz 环境配置相关工作
- fuzz 执行阶段:fuzz 的主要执行过程
- 变异策略:测试用例的变异过程和方法
2. 文件架构
文件所包含的所有函数如下:
文件中声明和定义的函数数量较多,大部分单个函数的实现不会很难,但是需要将多个函数组合起来。
3. 函数源码分析
备注
代码中会有一些 APPLE 平台的逻辑处理和功能实现,但文章中将只分析 Linux 平台的逻辑实现,APPLE 的基本一致,没有太大差别。
1. 变量说明
文件前面声明了很多全局变量,大部分是跟 UI 相关的,其他的一部分是与程序选项相关的内容,我们不会单独拿出来进行介绍,在后续的函数中涉及到前面的全局变量我们会进行特殊介绍。
2. 初始配置
2.1 选项处理
main 函数是整个 AFL 的入口,第一个 while 循环:
while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "+i:o:f:m:b:t:T:dnCB:S:M:x:QV")) > 0)
... ...
)
该循环主要是通过 getopt 函数获取命令行输入的参数选项,然后根据不同的参数选项,在不同的 case 中进行不同的处理,例如 case 'i',获取种子文件的目录路径。
2.2 setup_signal_handlers
信号处理函数,设置各种信号句柄。设置处理的各种信号如下:
| 信号 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| SIGHUP/SIGINT/SIGTERM | 处理各种“stop”情况 |
| SIGALRM | 处理超时的情况 |
| SIGWINCH | 处理窗口大小 |
| SIGUSER1 | skip entry |
| SIGSTP/SIGPIPE | 没啥用的信号:) |
2.3 check_asan_opts
读取环境变量 ASAN_OPTIONS 和 MSAN_OPTIONS ,根据读取结果进行一些简单的正确性检查。(ASAN 和 MASN 我们会看情况进行深入讲解,现在可以理解为错误记录器。)
2.4 fix_up_sync
如果通过 -M或者-S指定了 sync_id,则更新 out_dir 和 sync_dir 的值:设置 sync_dir 的值为 out_dir,设置 out_dir 的值为out_dir/sync_id。这里主要就是对 -M/S 选项进行处理,这两个选项的作用我们会在应用时再进行介绍。
2.5 几个环境变量的设置
接下来是几个环境变量的读取,然后赋值给对应的变量:
if (getenv("AFL_NO_FORKSRV")) no_forkserver = 1;
if (getenv("AFL_NO_CPU_RED")) no_cpu_meter_red = 1;
if (getenv("AFL_NO_ARITH")) no_arith = 1;
if (getenv("AFL_SHUFFLE_QUEUE")) shuffle_queue = 1;
if (getenv("AFL_FAST_CAL")) fast_cal = 1;
if (getenv("AFL_HANG_TMOUT")) {
hang_tmout = atoi(getenv("AFL_HANG_TMOUT"));
if (!hang_tmout) FATAL("Invalid value of AFL_HANG_TMOUT");
}
if (dumb_mode == 2 && no_forkserver)
FATAL("AFL_DUMB_FORKSRV and AFL_NO_FORKSRV are mutually exclusive");
if (getenv("AFL_PRELOAD")) {
setenv("LD_PRELOAD", getenv("AFL_PRELOAD"), 1);
setenv("DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES", getenv("AFL_PRELOAD"), 1);
}
if (getenv("AFL_LD_PRELOAD"))
FATAL("Use AFL_PRELOAD instead of AFL_LD_PRELOAD");
2.6 save_cmdline ()
copy 一份当前的 cmdline 参数数据,然后申请一片内存进行保存,保存在 buf 处。
2.7 check_if_tty
读取环境变量 AFL_NO_UI,读取成功,设置 not_on_tty=1,然后返回;调用 ioctl 来读取窗口大小,读取报错 ENOTTY,表明没有运行在一个 tty 上,设置 not_on_tty=1
2.8 CPU检查相关函数
- get_core_count(): 通过
sysctl函数来获取 CPU 核数 - check_crash_handling(): 确保核心转储不会进入程序,这里也就是运行 AFL 是需要修改
/proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern的检查位置,将该文件内容设置为 core 主要是为了避免计算机把 crash 误认成超时。 - check_cpu_governor(): 该函数主要检查 CPU governor 相关内容,在 fuzz 过程中基本不太常遇见。
2.9 setup_shm
设置共享内存和 virgin_bits(这里可以理解为初始的计算覆盖率的bit的初始值),我们结合源码进行解读:
EXP_ST void setup_shm(void) {
u8* shm_str;
if (!in_bitmap) memset(virgin_bits, 255, MAP_SIZE);
memset(virgin_tmout, 255, MAP_SIZE);
memset(virgin_crash, 255, MAP_SIZE);
shm_id = shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, MAP_SIZE, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0600);
if (shm_id < 0) PFATAL("shmget() failed");
atexit(remove_shm);
shm_str = alloc_printf("%d", shm_id);
if (!dumb_mode) setenv(SHM_ENV_VAR, shm_str, 1);
ck_free(shm_str);
trace_bits = shmat(shm_id, NULL, 0);
if (trace_bits == (void *)-1) PFATAL("shmat() failed");
}
- 如果
in_bitmap为空,也就是还没有进行过初始化,使用memset函数初始化数组vitgin_bits[MAP_SIZE]的每个元素的值为255,也就是\xff; - 连用两个
memset将vigrin_tmout[MAP_SIZE]和vigrin_crash[MAP_SIZE]进行初始化,每个元素同样设置成255, 也就是\xff; - 调用函数
shmget(IPC_PRIVATE, MAP_SIZE, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0600)来分配一块新的共享内存,返回标识保存在shm_id变量中; - 使用
atexit(remove_shm)来注册一个remove_shm函数,该函数会在 main 函数执行结束程序退出时自动执行,在remove_shm函数中则是调用了shmctl(shm_id, IPC_RMID,NULL)来处理我们这里开辟的共享内存; - 如果不是
dumb_mode,就设置环境变量SHM_ENV_VAR的值为shm_str,也就是开辟的共享内存地址; - 调用函数
shmat(shm_id, NULL, 0)设置trace_bits的值。在第一次创建完共享内存后,它还不能被任何进程访问使用,通过 shmat 函数可以将共享内存映射到当前进程的地址空间,这样就可以去使用共享内存了。trace_bits变量是用作SHM with instrumentation bitmap。
在这里是通过 trace_bits 和 virgin_bits 两个 bitmap 来分别记录当前的 tuple 信息和整体 tuple 信息,此外,这里还有几个关于共享内存的函数需要大家理解一下。
2.10 init_count_class16
这个函数比较有意思,trace_bits 用一个字节来记录是否到达路径和这个路径被命中了多少次,而这个次数在0-255之间,但比如一个循环,它循环5次和循环6次可能是完全一样的效果,为了避免被当成不同的路径,或者说尽可能减少因为命中次数导致的区别。所以在每次去计算是否发现了新路径之前,先把这个路径命中数进行规整,比如把命中5次和6次都统一认为是命中了8次:
static const u8 count_class_lookup8[256] = {
[0] = 0,
[1] = 1,
[2] = 2,
[3] = 4,
[4 ... 7] = 8,
[8 ... 15] = 16,
[16 ... 31] = 32,
[32 ... 127] = 64,
[128 ... 255] = 128
};
在进行规整时, AFL 是一次读取两个字节来进行处理,这样可以提升效率,函数源码如下:
EXP_ST void init_count_class16(void) {
u32 b1, b2;
for (b1 = 0; b1 < 256; b1++)
for (b2 = 0; b2 < 256; b2++)
count_class_lookup16[(b1 << 8) + b2] =
(count_class_lookup8[b1] << 8) |
count_class_lookup8[b2];
}
2.11 setup_dirs_fds
该函数主要用于准备输出文件夹和文件描述符:
EXP_ST void setup_dirs_fds(void) {
u8* tmp;
s32 fd;
ACTF("Setting up output directories...");
if (sync_id && mkdir(sync_dir, 0700) && errno != EEXIST)
PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", sync_dir);
if (mkdir(out_dir, 0700)) {
if (errno != EEXIST) PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", out_dir);
maybe_delete_out_dir();
} else {
if (in_place_resume)
FATAL("Resume attempted but old output directory not found");
out_dir_fd = open(out_dir, O_RDONLY);
... ...
}
/* Queue directory for any starting & discovered paths. */
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/queue", out_dir);
if (mkdir(tmp, 0700)) PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", tmp);
ck_free(tmp);
/* Top-level directory for queue metadata used for session
resume and related tasks. */
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/queue/.state/", out_dir);
if (mkdir(tmp, 0700)) PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", tmp);
ck_free(tmp);
/* Directory for flagging queue entries that went through
deterministic fuzzing in the past. */
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/queue/.state/deterministic_done/", out_dir);
if (mkdir(tmp, 0700)) PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", tmp);
ck_free(tmp);
/* Directory with the auto-selected dictionary entries. */
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/queue/.state/auto_extras/", out_dir);
if (mkdir(tmp, 0700)) PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", tmp);
ck_free(tmp);
/* The set of paths currently deemed redundant. */
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/queue/.state/redundant_edges/", out_dir);
if (mkdir(tmp, 0700)) PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", tmp);
ck_free(tmp);
/* The set of paths showing variable behavior. */
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/queue/.state/variable_behavior/", out_dir);
if (mkdir(tmp, 0700)) PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", tmp);
ck_free(tmp);
/* Sync directory for keeping track of cooperating fuzzers. */
if (sync_id) {
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/.synced/", out_dir);
if (mkdir(tmp, 0700) && (!in_place_resume || errno != EEXIST))
PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", tmp);
ck_free(tmp);
}
/* All recorded crashes. */
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/crashes", out_dir);
if (mkdir(tmp, 0700)) PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", tmp);
ck_free(tmp);
/* All recorded hangs. */
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/hangs", out_dir);
if (mkdir(tmp, 0700)) PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", tmp);
ck_free(tmp);
/* Generally useful file descriptors. */
dev_null_fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDWR);
if (dev_null_fd < 0) PFATAL("Unable to open /dev/null");
dev_urandom_fd = open("/dev/urandom", O_RDONLY);
if (dev_urandom_fd < 0) PFATAL("Unable to open /dev/urandom");
/* Gnuplot output file. */
tmp = alloc_printf("%s/plot_data", out_dir);
fd = open(tmp, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_EXCL, 0600);
if (fd < 0) PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", tmp);
ck_free(tmp);
plot_file = fdopen(fd, "w");
if (!plot_file) PFATAL("fdopen() failed");
fprintf(plot_file, "# unix_time, cycles_done, cur_path, paths_total, "
"pending_total, pending_favs, map_size, unique_crashes, "
"unique_hangs, max_depth, execs_per_sec\n");
/* ignore errors */
}
- 如果存在
sync_id,且创建sync_dir文件夹成功(权限为700,读写执行); - 创建
out_dir,权限为700,创建成功则获取out_dir_fd; - 创建
out_dir/queue文件夹,权限为 700: - 创建
out_dir/queue/.state文件夹,权限为 700; - 在
out_dir/queue/.state文件夹下依次创建deterministic_done, auto_extras/, redundant_edges/, variable_behavior/这几个字文件夹,作用在源码中都有说明,这里不过多解释; - 如果存在
sync_id,创建out_dir/.sysnced文件夹,权限为700,用于跟踪 cooperating fuzzers,这是一个同步用的文件夹; - 创建
out_dir/crashes文件夹,权限为700, 这是记录crashes 的文件夹; - 创建
out_dir/hangs文件夹,权限为700,这里记录 hangs; - 再获取几个常用的 fd:
/dev/null, /dev/urandom; - 只读打开
out_dir/plot_data文件,文件不存在就新建一个;然后向其中写入\# unix_time, cycles_done, cur_path, paths_total, pending_total, pending_favs, map_size, unique_crashes, unique_hangs, max_depth, execs_per_sec\n。
该函数会将 fuzz 使用的几个文件夹都进行设置,后续在 fuzz 过程中会频繁使用这些文件夹和文件。
2.12 read_testcases
该函数主要是从输入文件夹中读取测试用例放入到 queue 中:
static void read_testcases(void) {
struct dirent **nl;
s32 nl_cnt;
u32 i;
u8* fn;
/* Auto-detect non-in-place resumption attempts. */
fn = alloc_printf("%s/queue", in_dir);
if (!access(fn, F_OK)) in_dir = fn; else ck_free(fn);
ACTF("Scanning '%s'...", in_dir);
nl_cnt = scandir(in_dir, &nl, NULL, alphasort);
if (nl_cnt < 0) {
if (errno == ENOENT || errno == ENOTDIR)
... ...
}
if (shuffle_queue && nl_cnt > 1) {
ACTF("Shuffling queue...");
shuffle_ptrs((void**)nl, nl_cnt);
}
for (i = 0; i < nl_cnt; i++) {
struct stat st;
u8* fn = alloc_printf("%s/%s", in_dir, nl[i]->d_name);
u8* dfn = alloc_printf("%s/.state/deterministic_done/%s", in_dir, nl[i]->d_name);
u8 passed_det = 0;
free(nl[i]); /* not tracked */
if (lstat(fn, &st) || access(fn, R_OK))
PFATAL("Unable to access '%s'", fn);
/* This also takes care of . and .. */
if (!S_ISREG(st.st_mode) || !st.st_size || strstr(fn, "/README.testcases")) {
ck_free(fn);
ck_free(dfn);
continue;
}
if (st.st_size > MAX_FILE)
FATAL("Test case '%s' is too big (%s, limit is %s)", fn,
DMS(st.st_size), DMS(MAX_FILE));
if (!access(dfn, F_OK)) passed_det = 1;
ck_free(dfn);
add_to_queue(fn, st.st_size, passed_det);
}
free(nl); /* not tracked */
if (!queued_paths) {
... ...
}
last_path_time = 0;
queued_at_start = queued_paths;
}
- 首先检查
in_dir/queue的可访问权限,拿到 fd; - 扫描
in_dir,结果保存在结构体nl中,这是一个dirent结构; - 使用 for 循环遍历
nl,其中nl[i]->d_name的值为in_dir文件夹下的文件名字的字符串,把每个文件名赋值给fn,u8 *dfn = alloc_printf("%s/.state/deterministic_done/%s", in_dir, nl[i]->d_name); - 通过文件属性过滤掉
.和..这样的regular文件,并检查文件大小,如果文件大小大于MAX_FILE,默认是1024*1024字节,即1M; - 通过
access检查in_dir/.state/deterministic_done/nl[i]->d_name是否存在; - 调用
add_to_queue(fn. st.st_size, passwd_det)添加到 queue 中; - 如果
queued_paths不存在,表示输入文件夹为0,抛出异常; - 设置
last_path_time为 0; - 设置
queued_at_start = queued_paths,这是所有初始阶段的 input 的值。
2.13 load_auto
该函数会加载生成的提取出来的字典的 token :
static void load_auto(void) {
u32 i;
for (i = 0; i < USE_AUTO_EXTRAS; i++) {
u8 tmp[MAX_AUTO_EXTRA + 1];
u8* fn = alloc_printf("%s/.state/auto_extras/auto_%06u", in_dir, i);
s32 fd, len;
fd = open(fn, O_RDONLY, 0600);
if (fd < 0) {
if (errno != ENOENT) PFATAL("Unable to open '%s'", fn);
ck_free(fn);
break;
}
len = read(fd, tmp, MAX_AUTO_EXTRA + 1);
if (len < 0) PFATAL("Unable to read from '%s'", fn);
if (len >= MIN_AUTO_EXTRA && len <= MAX_AUTO_EXTRA)
maybe_add_auto(tmp, len);
close(fd);
ck_free(fn);
}
if (i) OKF("Loaded %u auto-discovered dictionary tokens.", i);
else OKF("No auto-generated dictionary tokens to reuse.");
}
- for 循环遍历从 0 到
USE_AUTO_EXTRAS,默认为 50;- 只读模式打开
alloc_printf("%s/.state/auto_extras/auto_%06u", in_dir, i)文件; - 打开成功,则从fd读取最多
MAX_AUTO_EXTRA+1个字节到tmp数组里,默认MAX_AUTO_EXTRA为32,这是单个auto extra文件的最大大小,读取出的长度保存到len里。 - 调用
maybe_add_auto(tmp, len)函数;
- 只读模式打开
2.14 pivot_inputs
该函数主要是为输入在输出文件夹中创建 hard link:
static void pivot_inputs(void) {
struct queue_entry* q = queue;
u32 id = 0;
ACTF("Creating hard links for all input files...");
while (q) {
u8 *nfn, *rsl = strrchr(q->fname, '/');
u32 orig_id;
if (!rsl) rsl = q->fname; else rsl++;
... ...
if (!strncmp(rsl, CASE_PREFIX, 3) &&
sscanf(rsl + 3, "%06u", &orig_id) == 1 && orig_id == id) {
u8* src_str;
u32 src_id;
resuming_fuzz = 1;
nfn = alloc_printf("%s/queue/%s", out_dir, rsl);
/* Since we're at it, let's also try to find parent and figure out the
appropriate depth for this entry. */
src_str = strchr(rsl + 3, ':');
if (src_str && sscanf(src_str + 1, "%06u", &src_id) == 1) {
struct queue_entry* s = queue;
while (src_id-- && s) s = s->next;
if (s) q->depth = s->depth + 1;
if (max_depth < q->depth) max_depth = q->depth;
}
} else {
#ifndef SIMPLE_FILES
u8* use_name = strstr(rsl, ",orig:");
if (use_name) use_name += 6; else use_name = rsl;
nfn = alloc_printf("%s/queue/id:%06u,orig:%s", out_dir, id, use_name);
#else
nfn = alloc_printf("%s/queue/id_%06u", out_dir, id);
#endif /* ^!SIMPLE_FILES */
}
/* Pivot to the new queue entry. */
link_or_copy(q->fname, nfn);
ck_free(q->fname);
q->fname = nfn;
/* Make sure that the passed_det value carries over, too. */
if (q->passed_det) mark_as_det_done(q);
q = q->next;
id++;
}
if (in_place_resume) nuke_resume_dir();
}
- 创建队列结构
struct queue_entry* q = queue,初始化id = 0; while循环遍历 queue :- 在
q-fname中找到最后一个/,找不到则rsl = q->fname,否则rsl指向/后的第一个字符; - 比较
rsl中的前 3 个字符,是否与id_相同- 如果相同,则设置
resuming_fuzz = 1,然后进行一些恢复操作; - 如果不相同,再再
rsl中寻找,org:字符串,找到则将user_name指向该字符串冒号后的名字,没有找到则user_name = rsl; - 设置
nfn = alloc_printf("%s/queue/id:%06u,orig:%s", out_dir, id, use_name);
- 如果相同,则设置
- 修改
q->fname指向上面创建的 hard link; - 判断
q->passed_det的值,如果为1, 则进行mark_as_det_done(q)。该函数主要是打开out_dir/queue/.state/deterministic_done/use_name这个文件,如果不存在就创建这个文件,然后设置q的passed_det为1。user_name就是orig:后面的字符串。 - 判断是否设置了
in_place_resume,如果进行了设置,则nuke_resume_dir(),而该函数主要执行的是一些删除操作:- 删除
out_dir/_resume/.state/deterministic_done文件夹下所有id:前缀的文件 - 删除
out_dir/_resume/.state/auto_extras文件夹下所有auto_前缀的文件 - 删除
out_dir/_resume/.state/redundant_edges文件夹下所有id:前缀的文件 - 删除
out_dir/_resume/.state/variable_behavior文件夹下所有id:前缀的文件 - 删除文件夹
out_dir/_resume/.state - 删除
out_dir/_resume文件夹下所有id:前缀的文件 - 如果全部删除成功就正常返回,如果有某一个删除失败就抛出异常。
- 删除
- 在
我们思考一下为什么要使用硬链接的方式将输入文件夹中的文件都映射到输出文件夹中去?AFL 本身在 fuzz 过程中会涉及到很重的各种磁盘读取操作,如果输入输出在不同的路径下,会加重磁盘读取的一系列操作,这样做是为了减轻磁盘读取负担,也是为了加快 fuzz 的效率。而之所以设置成输入输出在不同的目录下,个人认为只是为了方便归档。
2.15 load_extras
从 extras 目录中读取 extras 并按大小对其进行排序,代码比较简单,这里不做过多赘述。
2.16 find_timeout
该函数里有一个全局变量 timeout_given,该变量是可以用户指定的超时时间。用户如果没有用 -t 选项来指定超时时间时,AFL 不能一遍又一遍地在每次 resuming session 时去调整超时时间,该函数就是为了防止超时值因为随机波动而发生不受控增长的问题。
static void find_timeout(void) {
static u8 tmp[4096]; /* Ought to be enough for anybody. */
u8 *fn, *off;
s32 fd, i;
u32 ret;
if (!resuming_fuzz) return;
if (in_place_resume) fn = alloc_printf("%s/fuzzer_stats", out_dir);
else fn = alloc_printf("%s/../fuzzer_stats", in_dir);
fd = open(fn, O_RDONLY);
ck_free(fn);
if (fd < 0) return;
i = read(fd, tmp, sizeof(tmp) - 1); (void)i; /* Ignore errors */
close(fd);
off = strstr(tmp, "exec_timeout : ");
if (!off) return;
ret = atoi(off + 20);
if (ret <= 4) return;
exec_tmout = ret;
timeout_given = 3;
}
- 首先判断
resuming_fuzz变量,如果为0表示不在 resuming session 模式,直接返回; - 判断
in_place_resume变量,如果为1, 则设置fn = alloc_printf("%s/fuzzer_stats", out_dir);,否则fn = alloc_printf("%s/../fuzzer_stats", in_dir); - 只读模式读取
fd内容到tmp[4096]中,并搜索exec_timeout:字符串,如果找不到直接返回,如果找到了则读取这个超时时间,大于4就设置为exec_tmout。
2.17 detect_file_args
该函数主要是检查参数选项中有没有 @@ 符号,如果存在则替换为 out_dir/.cur_input ,没有直接返回。@@ 符号是我们在运行 AFL 时,会把输入文件夹中的测试用例当作参数来放在命令行中。
2.18 setup_stdio_file
该函数主要是处理用户没有指定 -f 参数时,会删除原本的 out_dir/.cur_input,然后创建一个新的 out_dir/.cur_input,并保存其文件描述符在 out_fd 中。
2.19 check_binary
遍历路径搜索二进制格式的目标文件,并且会校验该文件是ELF格式文件而不是shell文件,同时还会检查程序是否进行了插桩。
阶段总结
到这里为止,对于基本环境配置已经完成,涉及到的关键函数如下:
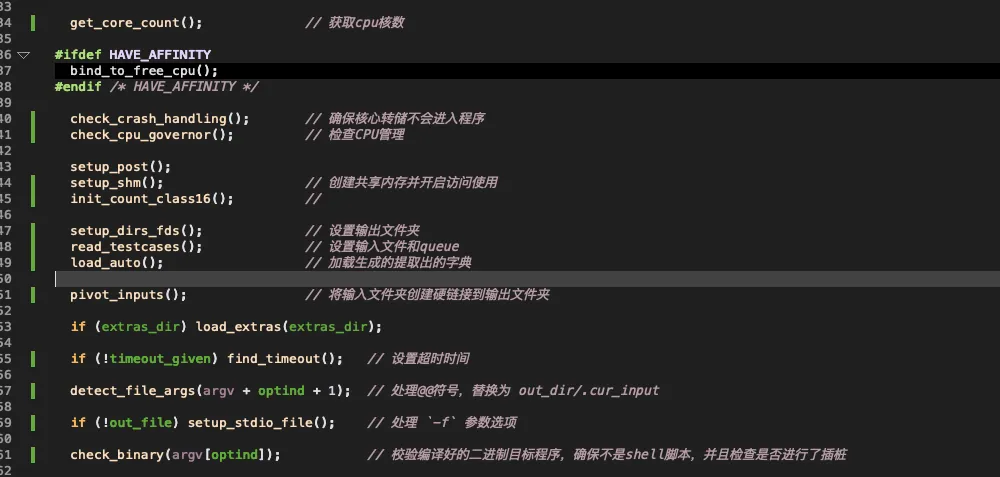
每个函数会进行一部分内容的初始化设置,并且在此之前还有一些环境变量的设置。
从此往后,就与实际的 fuzz 过程紧密联系,我们在后续文章中会逐步介绍 fuzz 的实际执行过程。
